

Nitrate would be the less soluble ion (from energy concerns) in agreement with Fajan's rules. The slight positive charge on the carbon will be larger if it is attached to a chlorine. Silver Nitrate is a highly water soluble crystalline Silver source for uses compatible with nitrates and lower (acidic) pH. This arrangement is commonly used as an example of resonance. This charge results from a combination formal charge in which each of the three oxygens carries a 23 charge, whereas the nitrogen carries a +1 charge, all these adding up to formal charge of the polyatomic nitrate ion. (There's also - related to Fajan I think - the HSAB concept which tries to extend also to hard-hard unsoluble salts [e.g. REACTIONS INVOLVING HALOGENOALKANES AND SILVER NITRATE SOLUTION. The nitrate ion carries a formal charge of 1.
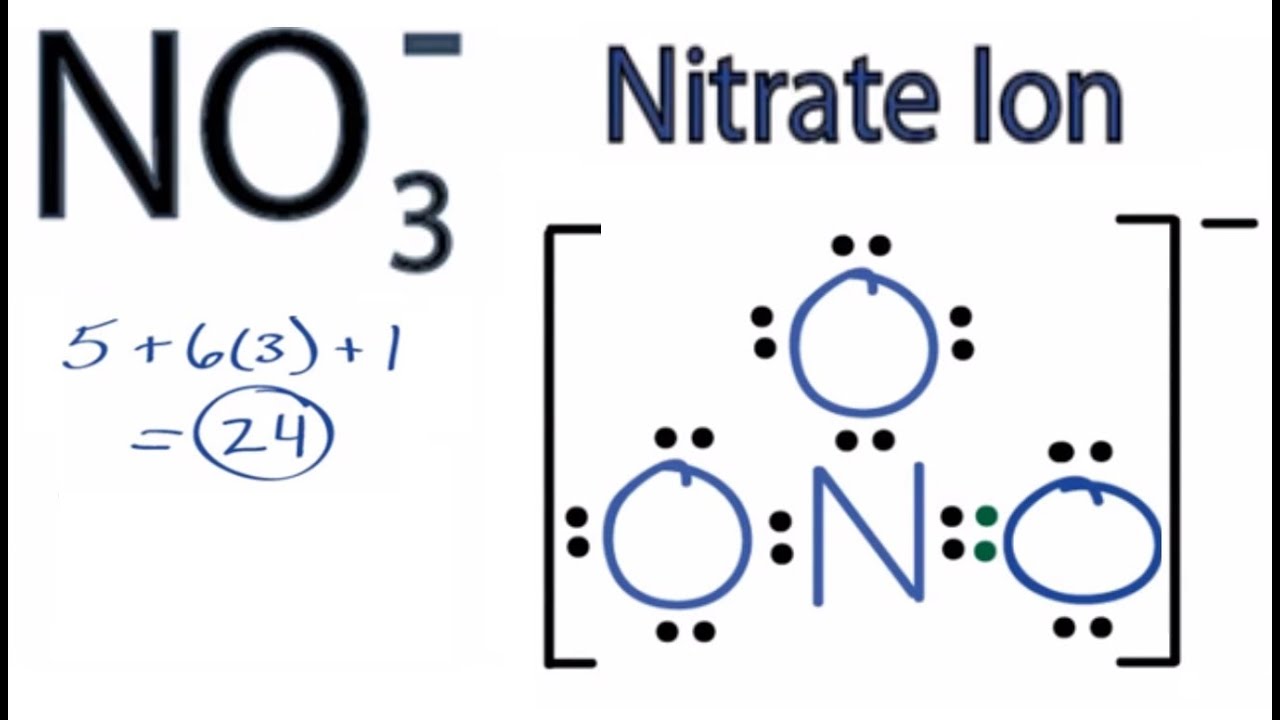
So in the case of the nitrate, usually good solubility of nitrates seem to win over the usually not so good solubility of silver salts.įor the Chloride, it is maybe similar: the Chloride stands between the good solubility of AgF and the low solubility of AgBr.

Sulfate, carbonate, oxide, sulfide (of course), even the stochiometric cyanide (if I remember correctly) isn't soluble. On the other hand, silver salts in general aren't well soluble (I recall only fluoride, nitrate and perchlorate as soluble. This is often explained by the exceptionally good delocalization of the negative charge. KEY FACTS OTHER NAMES: Silver (I) nitrate lunar caustic FORMULA: AgNO 3 ELEMENTS: Silver, nitrogen, oxygen COMPOUND TYPE: Salt (inorganic) STATE: Solid MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 169. I'm afraid this is rather a non-answer (or why is it so difficult to answer this). KEY FACTS OTHER NAMES: Silver (I) nitrate lunar caustic FORMULA: AgNO 3 ELEMENTS: Silver, nitrogen, oxygen COMPOUND TYPE: Salt (inorganic) STATE: Solid MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 169.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
